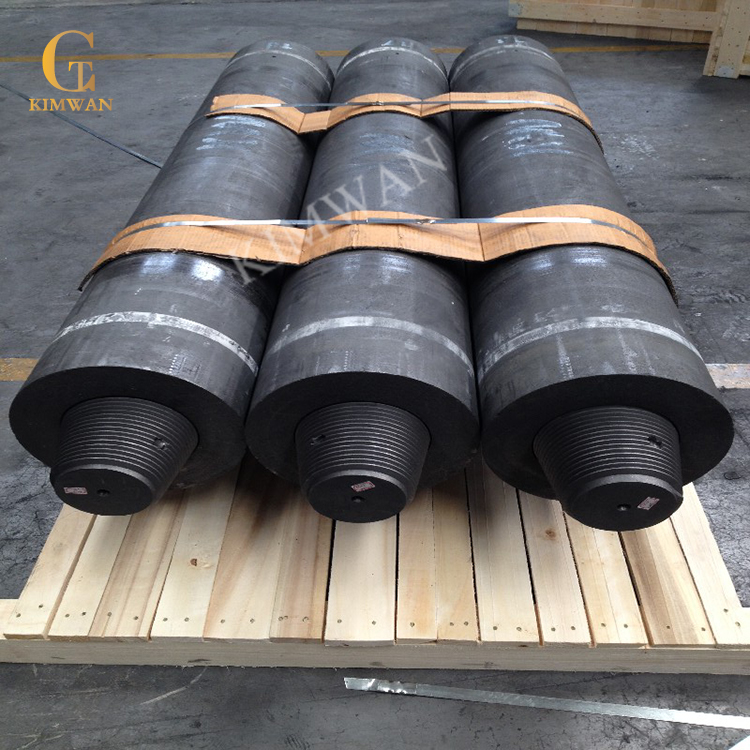
Graphite Electrode
At present, the steelmaking methods used in countries around the world are mainly converter steelmaking (mainly oxygen top-blown converters) and electric arc furnace steelmaking. Electric furnace steelmaking uses electric energy as a heat source for smelting. The most commonly used electric furnaces are electric arc furnaces and induction furnaces. Electric arc furnace steelmaking accounts for the vast majority of electric furnace steel production. The electric furnace generally referred to as an electric arc furnace.
Graphite Electrode
Electric furnace steelmaking is the main method for producing special steel at home and abroad. Electric arc furnace steelmaking is a method of inputting electric energy into an electric arcmaking furnace through a graphite electrode, and also a method of steelmaking by using the heat generated by the electric arc between the end of the electrode and discharge among furnace material.

Graphite Electrode
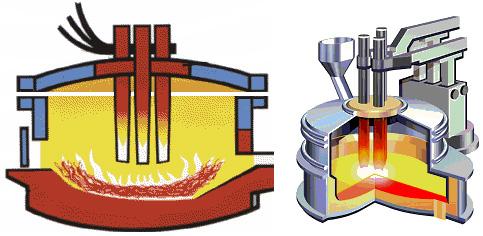
Graphite electrode schematic
The graphite electrode is mainly made of petroleum coke and needle coke, and the coal bitumen is used as a binder. It is made by calcination, compounding, kneading, pressing, roasting, graphitization and machining. It is the conductor to heat and melt by discharging electric energy in the form of electric arc in the electric arc furnace. Compared with the traditional electrode material, the graphite electrode has the advantages of good processing performance, easy polishing, low electrode consumption, fast discharge speed, light weight, high temperature resistance, small electrode deformation, easy clearing angle, etc. .
Advantages of graphite electrodes
(1): The increasing complexity of mold geometries and the diversification of product applications have led to higher and higher requirements for the discharge accuracy of spark machines. The advantages of the graphite electrode are that the processing is easier, the discharge processing removal rate is high, and the graphite loss is small. Therefore, some group-based spark machine customers give up the copper electrode and switch to the graphite electrode. In addition, some special shaped electrodes cannot be made of copper, but graphite is easier to form, and copper electrodes are heavier and not suitable for processing large electrodes. These factors have caused some group-based spark machine customers to apply graphite electrodes.
(2): Graphite electrodes are easier to process, and the processing speed is significantly faster than copper electrodes. For example, the use of milling technology to process graphite, the processing speed is 2 to 3 times faster than other metal processing and does not require additional manual processing, while the copper electrode needs manual frustration. Similarly, if a high-speed graphite machining center is used to make the electrode, the speed will be faster, the efficiency will be higher, and no dust problem will occur. In these processes, selecting the right hardness tool and graphite can reduce the tool wear loss and copper breakage. If the milling time of the graphite electrode and the copper electrode graphite electrode is specifically compared, the graphite is 67% faster than the copper electrode. In the general discharge machining, the graphite electrode is processed 58% faster than the copper electrode. As a result, the processing time is greatly reduced, and the manufacturing cost is also reduced.
(3): The design of the graphite electrode is different from that of the conventional copper electrode. Many mold shops usually have different reserves for roughing and finishing of copper electrodes, while graphite electrodes use almost the same amount of reservation, which reduces the number of CAD/CAM and machining times. For this reason alone, it is sufficient to improve the accuracy of the mold cavity to a large extent.
Tianjin Kimwan Carbon Technology & Development Co., Ltd.., the predecessor was established in 1998. The company is mainly engaged in research, development, production and sales of special new carbon and graphite materials, and has 12 patents.
The main raw material for graphite electrode production is petroleum coke. The ordinary power graphite electrode can be added with a small amount of pitch coke. The sulfur content of petroleum coke and pitch coke cannot exceed 0.5%. Needle coke is also required for the production of high power or ultra high power graphite electrodes. The main raw material for aluminum anode production is petroleum coke, and the control of sulfur content is not more than 1.5% to 2%. Petroleum coke and pitch coke should meet the relevant national quality standards.
The main products of our company's graphite electrode are: ordinary graphite electrode, high-power graphite electrode, ultra-high power graphite electrode, etc. The company holds ISO9001, TS16949 quality system, environmental management system ISO14001 and OHSAS18001 certification for occupational health and safety management system. With the advantage of production capacity, the products have superior prices and relatively long life, resulting in strong competitiveness. So far, product sales have covered more than 50 regions including the United States, Japan, Germany, and India, and have established long-term supply and demand relationships with many large domestic enterprises. Free consultation, graphite electrode quotes are available at any time.
HP Graphite Electrode For STEEL
技術(shù)指標(biāo):Technical indicators:
普通功率石墨電極技術(shù)指標(biāo):General power graphite electrode technical indicators:
指標(biāo)index |
單位unit |
公稱直徑(mm) |
||||
75-130 |
150-200 |
250-350 |
400-500 |
|||
電阻率Resistivity |
電極electrode |
μΩm |
8.5 |
9.0 |
9.0 |
9.0 |
接頭Connector |
8.5 |
8.5 |
8.5 |
8.5 |
||
抗折強度Flexural strength |
電極electrode |
MPa |
9.8 |
9.8 |
7.8 |
6.4 |
接頭Connector |
13 |
13 |
13 |
13 |
||
彈性模量Elastic Modulus |
電極electrode |
GPa |
9.3 |
9.3 |
9.3 |
9.3 |
接頭Connector |
14 |
14 |
14 |
14 |
||
灰分Ash |
電極electrode |
% |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
接頭connector |
||||||
體積密度Bulk density |
電極electrode |
g/cm3 |
1.58 |
1.52 |
1.52 |
1.52 |
接頭connector |
1.63 |
1.63 |
1.68 |
1.68 |
||
熱膨脹系數(shù)Thermal expansion coefficient |
電極electrode |
10-6 1/℃ |
2.9 |
2.9 |
2.9 |
2.9 |
接頭connector |
2.8 |
2.8 |
2.8 |
2.8 |
允許電流:Allowable current:
公稱直徑(mm)Nominal diameter (mm) |
允許電流(A)Allowable current(A) |
200 |
5000-6900 |
250 |
7000-10000 |
300 |
10000-13000 |
350 |
13500-18000 |
400 |
18000-23500 |
450 |
22000-27000 |
500 |
25000-32000 |
高功率石墨電極技術(shù)指標(biāo):High power graphite electrode technical indicators:
指標(biāo)Index |
單位unit |
公稱直徑 300-500mm Nominal Diameter |
|
電阻率Resistivity |
電極electrode |
μΩm |
7.0 |
接頭connector |
6.5 |
||
抗折強度Flexural strength |
電極electrode |
MPa |
10.0 |
接頭connector |
14.0 |
||
彈性模量Elastic Modulus |
電極electrode |
GPa |
12.0 |
接頭connector |
16.0 |
||
灰分Ash |
電極electrode |
% |
0.3 |
接頭connector |
|||
體積密度bulk density |
電極electrode |
g/cm3 |
1.64 |
接頭connector |
1.72 |
||
熱膨脹系數(shù)Thermal expansion coefficient |
電極electrode |
10-6 1/℃ |
2.4 |
接頭connector |
2.2 |
允許電流:Allowable current
公稱直徑(mm)Nomical diameter(mm) |
允許電流(A)allowable current(A) |
300 |
13000-17400 |
350 |
17400-24000 |
400 |
21000-31000 |
450 |
25000-40000 |
500 |
30000-48000 |
準超高功率石墨電極技術(shù)指標(biāo): Quasi-ultra-high power graphite electrode technical indicators:
指標(biāo)Index |
單位Unit |
公稱直徑 350-500mm Nomical Diameter350-500mm |
|
電阻率Resistivity |
電極electrode |
μΩm |
6.0 |
接頭connector |
4.0 |
||
抗折強度Flexural strength |
電極electrode |
MPa |
12.0 |
接頭connector |
20.0 |
||
彈性模量Elastic Modulus |
電極electrode |
GPa |
12.0 |
接頭connector |
18.0 |
||
灰分Ash |
電極electrode |
% |
0.3 |
接頭connector |
|||
體積密度bulk density |
電極electrode |
g/cm3 |
1.65 |
接頭connector |
1.74 |
||
熱膨脹系數(shù)thermal expansion coefficient |
電極electrode |
10-6 1/℃ |
1.90 |
接頭connector |
1.40 |
允許電流:Allowable current
公稱直徑(mm)Nominal Diameter(mm) |
允許電流(A)Allowable current(A) |
350 |
20000-30000 |
400 |
25000-40000 |
450 |
32000-45000 |
500 |
38000-55000 |
超高功率石墨電極技術(shù)指標(biāo): Ultra high power graphite electrode technical indicators:
指標(biāo)Index |
單位Unit |
公稱直徑 350-500mm Nominal Diameter 350-500mm |
|
電阻率Resistivity |
電極electrode |
μΩm |
5.8 |
接頭connector |
4.0 |
||
抗折強度Flexural strength |
電極electrode |
MPa |
12.0 |
接頭connnector |
20.0 |
||
彈性模量elastic modulus |
電極electrode |
GPa |
14.0 |
接頭connector |
18.0 |
||
灰分Ash |
電極electrode |
% |
0.3 |
接頭connector |
|||
體積密度bulk density |
電極electrode |
g/cm3 |
1.65 |
接頭connector |
1.74 |
||
熱膨脹系數(shù)thermal expansion coefficient |
電極electrode |
10-6 1/℃ |
1.5 |
接頭connector |
1.4 |
允許電流:Allowable current
公稱直徑(mm)Nominal Diameter |
允許電流(A)Allowable current(A) |
350 |
20000-30000 |
400 |
25000-40000 |
450 |
32000-45000 |
500 |
38000-55000 |
